 |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diet and ObesityObesityThe term obesity is applied to excessive deposition or distribution of fat in the body. Excess of fat is a disadvantage rather than as asset; it may lengthen the waist line, “but shortens the life line” of the individual by imposing an extra burden on the cardiovascular system. Who is Obese?Normally, men need up to 2,500 calories daily, while women and other inactive men need only about 2,000 calories daily. However, pregnant and nursing women needs about 300-500 more calories daily. Obesity is present in women whose body makeup is over 30 percent fast and in men whose bodies contain over 25 percent fat. Optimum body constitution is less than 24 percent body fat for women and less than 18 percent for men. Causes of ObesityThe main causes of obesity are described below:
Consuming more calories than are actually burned causes obesity. However, this imbalance between calories in and out may vary from person to person.
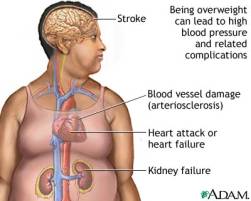
Obesity runs in family. For instance, children of obese parents are 10 times more likely to be obese than those children whose parents have normal weight! Obesity and HeartOur heart is continuously working and if someone is overweight; in that case, you can well imagine how much more the heart has to work. Hence, obesity causes the heart to work even more and can lead to heart attack. Why Obesity causes Heart attack?Obesity causes the wall of the heart's left ventricle to become thick which if persists can finally cause heart attack. It also increases the chances of developing other risk factors for heart disease, especially high blood pressure, and high blood cholesterol. Other Complications of ObesityThe other major complications of obesity include:
How common is Obesity?Obesity has become a very common problem all over the world. The rate of obesity has doubled in the last two decade. At present, every one in five is obese. Treatment of ObesitySince obesity is so common and produces so few symptoms in its earlier stages, it remains a personal but socially acceptable problem for most patients; scarcely seeming to merit the major effort involved in its correction. Basic Requirement for TreatmentThe basic requirement for the treatment of obesity, whether it occurs in infants, children or adults, is the regulation of daily intake of energy sources. In first instance an ‘unweighed diet’ is used, but if this is not effective, the stricter discipline of a ‘weighed diet’ may need to be imposed for a time. Maintaining Normal Weight for ObeseFor a previously obese person to maintain a normal weight often demands persisting indefinitely with some dietary restrictions, even when the target weight has been attained, the majority of patients are unable or unwilling to sustain the effort required. Exercise
Healthy Diet PlanIn order to loose your weight, you should follow a healthy diet plan. It may appear difficult to follow at start but will surely help you in reducing your weight. The diet plan is described below: Reduce Cholesterol IntakeCholesterol is an important part of a healthy body. But as it is said “excess of everything is bad”, similarly excess of cholesterol is also very dangerous. The saturated fat in our diet forms cholesterol. These are the animal fats such as meat (beef, pork, lamb etc) and dairy products (milk, butter, cheese etc.). It is a natural ingredient of some foods such as eggs, liver, kidney, prawns and fish. You should reduce the intake of these to one portion and maximum 3 eggs a week. Reduce Triglycerides IntakeExtra calories are stored in body as Triglycerides. It leads to bad health and many diseases.
Reduce Fat Intake
products such as skimmed milk, low fat cheese and diet yoghurts.
Reduce Sugar Intake
Increase Fibre Intake
Reduce Salt IntakeSalt pumps the extra fluid around the body and thus increases the work for heart. Therefore, to prevent heart diseases you should limit the use of salt. Tips to avoid salt:
 Remember to enjoy what you eat! Remember to enjoy what you eat!
|
|
|||||||||
Home © health-care-information.org. All rights reserved. Diseases | Drugs | Injuries | Medical Tests | Home Remedies | Herbal Medicines |
Disclaimer: Health-Care-Information.org is designed for educational purposes only and is not engaged in rendering medical advice or professional medical services. Any medical or other decisions should be made in consultation with your qualified health care provider. We will not be liable for any complications, injuries or other medical accidents arising from or in connection with the use of or reliance upon any information on this web site.